(HBO) - According to the Ministry of Health, Vietnam is now facing a serious hike in non-communicable diseases (NCDs). It is estimated that 7 out of every 10 people die of NCDs, mainly cardiovascular, cancer, diabetes and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The question is how health screening should be done to help avoid creating an economic burden for families and society?

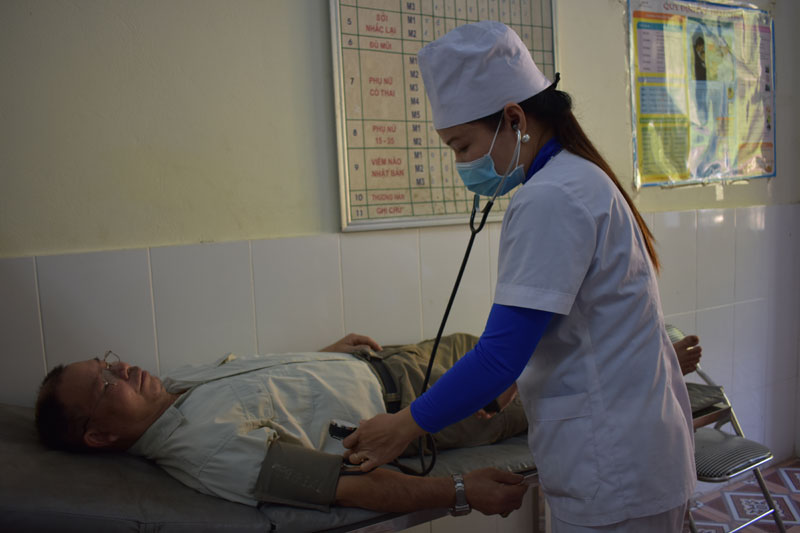
Personnel of Dong Bang Commune
Health Station (Mai Chau) carry out a periodical blood test for Luu Xuan Lich,
a resident in Tieu Khu hamlet, Dong Bang commune.
According to the health sector's
assessment, the people suffering from hypertension and diabetes account for
about 10 percent of the population. However, only about 30 percent of the patients
have been diagnosed and managed. Meanwhile, the grassroots-level health
facilities, particularly in communes and wards, have yet to provide adequate
services for early detection, diagnosis, treatment, and counseling, among
others. The service quality is limited due to a shortage of human resources and
essential drugs, particularly those treating diabetes and blood pressure
conditions.
Vu Thanh, Head of the NCD
Prevention and Control Department at the provincial Center for Disease Control,
said the management, detection and treatment of NCDs at the grassroots-level
facilities are important. The places help not only people with NCDs get better
health care and cut treatment costs, but also the entire system improve its
medical examination and treatment quality, he added.
Implementing the decisions by the Prime Minister and
the Ministry of Health on the prevention and control of NCDs, the centre has
developed a plan for the work until 2025. Accordingly, it focuses on boosting
relevant authorities’ responsibilities and people's awareness; strengthening interdisciplinary
coordination and the local capacity of NCDs prevention, monitoring, detection,
diagnosis, and treatment, among others. The plan aims at successfully
implementing health screening for NCDs at grassroots-level health facilities.
The emulation movement "Hoa Binh joining hands to build new-style rural areas” has been widely spreading, becoming a driving force that motivates the localities to renew rural landscapes and improve the material and spiritual lives of the residents. In this movement, the people play a central role-both as the main implementers and direct beneficiaries of its outcomes.
In response to the global digital revolution, Hoa Binh Newspaper is transforming itself into a modern and multi-platform media hub, blending cutting-edge technology with a restructured newsroom and a new generation of tech-savvy journalists.
Hoa Binh province’s Association of the Elderly recently held a conference to review the project on expanding the inter-generation self-help club model until 2025.
In a move to implement Resolution No. 57-NQ/TW, issued on December 22, 2024 by the Politburo, which targets breakthroughs in science-technology development, innovation, and digital transformation, the Hoa Binh provincial Department of Health has issued a plan to roll out the "Digital Literacy for All” campaign within the local health sector.
An Nghia Commune (Lạc Sơn District) is one of the communes that achieved the tha standard of the national new rural area in 2018. Entering a new development phase, the commune is now trying to meet the criteria for the advanced new rural development. With the strong political will and the public consensus, the commune is gradually overcoming the challenges to reach this goal, aiming for the sustainable development.



